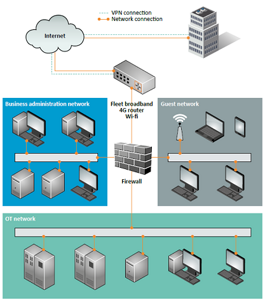
In order to improve Cyber Security on ships, we offer information on the new requirements for Cyber Security Onboard Ships.
Information Security - preservation of confidentiality, integrity and availability of information.
There are 3 (three) basic principles that information protection should provide:
- data integrity — protection against failures leading to the loss of information, as well as protection from unauthorized creation or destruction of data;
- confidentiality of information;
- availability of information for all authorized users.
Information security is a complex task aimed at ensuring security implemented by the implementation of the information security system. The problem of information security is multifaceted and complex and covers a number of important tasks. In addition, the problems of information security are constantly exacerbated by the processes of penetration into all spheres of society of technical means of data processing and transmission, and, above all, computer systems.
With the development of computer systems, failures or errors which can lead to serious consequences, computer security issues have become a priority. To date, information protection of the network has become almost as important as the safety and security of ships throughout the shipping sector.
Examples of risks related to Cyber Security include:
- risks of information leakage or distortion;
- risks of power failure;
- risks of cargo theft or spill;
risks of changes in exchange vessels.
The plans and procedures of the shipping company's for cyber security risk management should be aligned with existing risk management procedures which are regulated by ISM Code and ISPS.
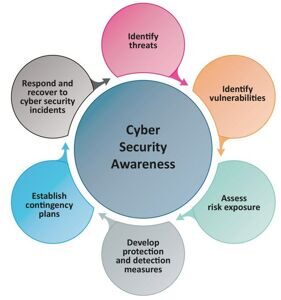
The development, understanding and awareness of key aspects of cyber security and safety are highlighted in figure below:
Cyber security approach:
- Identify threats
- Identify vulnerabilities
- Assess risk exposure
- Develop protection and detection measures
- Establish contingency plans
- Respond to and recover from cyber security incidents
These functional elements should be included in the overall risk management system. They reflect the necessary activities and desired results of effective cyber risk management with respect to critical systems involved in maritime operations.
The information protection system should be deployed at all levels of the company from shore management to crew members, and integrated with security and safety systems to ensure the effectiveness of ship operations.
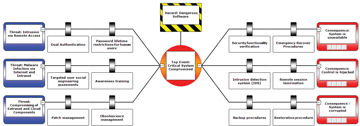
Example visualization of cyber security Bow-Tie components:
Potentially onboard vulnerable systems, equipment and technologies may include:
Communication systems:
- integrated communication systems
- satellite communication equipment
- Voice Over Internet Protocols (VOIP) equipment
- wireless networks (WLANs)
- public address and general alarm systems.
Bridge systems
- integrated navigation system
- positioning systems (GPS, etc.)
- Electronic Chart Display Information System (ECDIS)
- Dynamic Positioning (DP) systems
- systems that interface with electronic navigation systems and propulsion/ maneuvering systems
- Automatic Identification System (AIS)
- Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS)
- radar equipment
- Voyage Data Recorders (VDRs)
- other monitoring and data collection systems.
Propulsion and machinery management and power control systems
- engine governor
- power management
- integrated control system
- alarm system
- emergency response system.
Access control systems
- surveillance systems such as CCTV network
- Bridge Navigational Watch Alarm System (BNWAS)
- Shipboard Security Alarm Systems (SSAS)
- electronic “personnel-on-board” systems.
Cargo management systems
- Cargo Control Room (CCR) and its equipment
- level indication system
- valve remote control system
- ballast water systems
- water ingress alarm system.
Passenger servicing and management systems
- Property Management System (PMS)
- electronic health records
- financial related systems
- ship passenger/seafarer boarding access systems
- infrastructure support systems like domain naming system (DNS) and user authentication/ authorization systems.
Passenger-facing networks
- passenger Wi-Fi or LAN internet access
- guest entertainment systems
- passenger Wi-Fi or Local Area Network (LAN) internet access, for example where onboard personnel can connect their own devices18
- guest entertainment systems.
Core infrastructure systems
- security gateways
- routers
- switches
- firewalls
- Virtual Private Network(s) (VPN)
- Virtual LAN(s) (VLAN)
- intrusion prevention systems
- security event logging systems.
Administrative and crew welfare systems
- administrative systems
- crew Wi-Fi or LAN internet access, for example where onboard personnel can connect their own devices.
As part of the Safety Management System (SMS), our company offers you the development of appropriate plans and ship procedures for information protection on ships (Cyber Security Management Plan - CSP).